HRV and Stress Management: The Complete Guide
Ready to start tracking your HRV? Check out our top picks: Whoop | Oura Ring | Polar H10
HRV and Stress Management: The Complete Guide
In today's fast-paced world, stress has become an almost unavoidable part of daily life. While some stress can be beneficial, chronic stress takes a significant toll on both physical and mental health. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) has emerged as a powerful tool for understanding and managing stress. This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between HRV and stress, and how you can use HRV monitoring to develop more effective stress management strategies.
The Science of Stress and HRV
Understanding the Stress Response
When you encounter a stressor, your body activates the sympathetic branch of your autonomic nervous system - the "fight or flight" response. This triggers a cascade of physiological changes:
- Increased heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Heightened muscle tension
- Release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline
These responses are designed to help you deal with immediate threats. However, when stress becomes chronic, these same responses can become harmful.
How HRV Reflects Stress
Heart Rate Variability measures the variation in time between successive heartbeats. This variation is controlled by your autonomic nervous system:
- Sympathetic activity (fight or flight) tends to decrease HRV
- Parasympathetic activity (rest and digest) tends to increase HRV
When you're stressed, sympathetic activity dominates, resulting in lower HRV. This makes HRV an excellent objective measure of your body's stress state, often detecting stress before you're consciously aware of it.
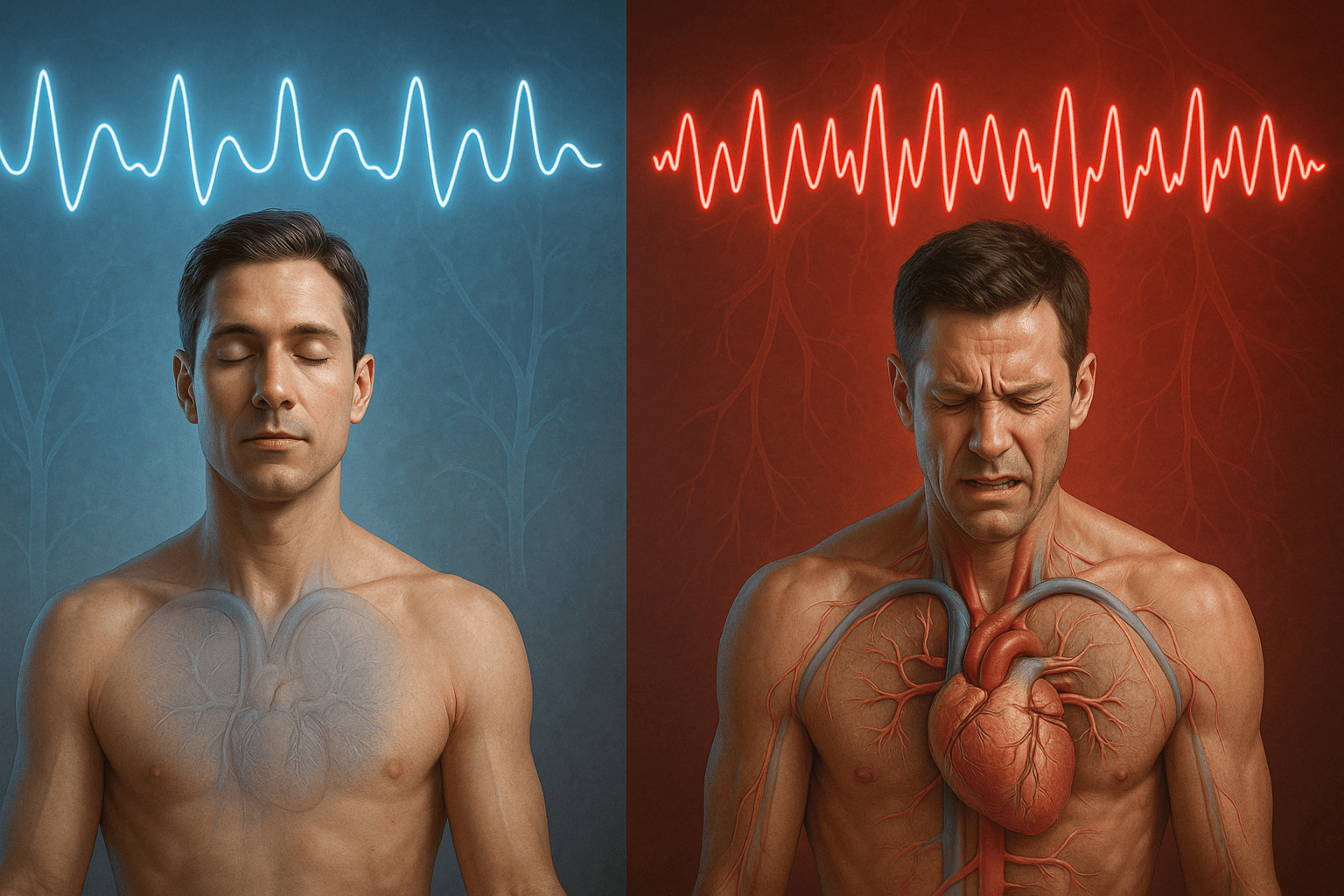
Measuring Stress Through HRV
HRV Metrics for Stress Assessment
Several HRV metrics are particularly useful for stress assessment:
- RMSSD (Root Mean Square of Successive Differences): A time-domain measure that reflects parasympathetic activity
- HF (High Frequency) Power: A frequency-domain measure associated with parasympathetic activity
- LF/HF Ratio: Often used as an indicator of sympathetic/parasympathetic balance
HRV Monitoring Devices for Stress
Several devices excel at tracking HRV for stress management:
- Whoop: Provides a daily stress score based on HRV and other metrics
- Oura Ring: Tracks nighttime HRV and provides readiness scores
- Polar H10 with HRV apps: Allows for spot-checks of HRV throughout the day
Interpreting Your HRV for Stress Management
Establishing Your Baseline
To effectively use HRV for stress management, you need to establish your personal baseline:
- Track your HRV consistently for 2-4 weeks
- Note the normal range and daily patterns
- Identify factors that influence your HRV
Remember that HRV is highly individual - what matters is how your current HRV compares to your own baseline, not someone else's numbers.
Recognizing Stress Patterns
Once you have a baseline, you can begin to identify stress patterns:
- Acute stress: Sudden drops in HRV that recover quickly
- Chronic stress: Consistently lower HRV over extended periods
- Stress accumulation: Gradually declining HRV over days or weeks
Many HRV users report being able to identify stressful events or periods before they consciously recognize feeling stressed.
Evidence-Based Strategies to Manage Stress and Improve HRV
Breathing Techniques
Controlled breathing directly activates the parasympathetic nervous system and can improve HRV in real-time:
- Resonance breathing: 6 breaths per minute (5 seconds inhale, 5 seconds exhale)
- Box breathing: Equal inhale, hold, exhale, and hold (e.g., 4 seconds each)
- 4-7-8 breathing: 4 second inhale, 7 second hold, 8 second exhale
Research highlight: A study in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that just 5 minutes of resonance breathing significantly increased HRV and reduced perceived stress.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Regular mindfulness practice has been shown to improve HRV and stress resilience:
- Start small: Even 5 minutes daily can be beneficial
- Be consistent: Daily practice is more effective than occasional longer sessions
- Use guided sessions: Apps like Calm, Headspace, or Waking Up can help beginners
Research highlight: A meta-analysis published in Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews found that mindfulness meditation consistently improved HRV parameters associated with stress regulation.

Physical Activity
Exercise has powerful effects on both HRV and stress management:
- Aerobic exercise: 150+ minutes weekly of moderate activity
- Zone 2 training: Low-intensity steady state cardio is particularly effective
- Nature exposure: Exercising outdoors provides additional stress-reduction benefits
Research highlight: Research in the International Journal of Sports Medicine found that regular aerobic exercise improved resting HRV and reduced physiological responses to stressors.
Sleep Optimization
Poor sleep and stress create a vicious cycle that HRV monitoring can help break:
- Consistent schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same times
- Sleep environment: Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet
- Wind-down routine: Develop a relaxing pre-sleep ritual
Research highlight: A study in Psychophysiology found that sleep quality was strongly associated with next-day HRV and stress resilience.
Nutrition for Stress Management
Diet affects HRV through multiple pathways:
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Colorful fruits and vegetables, fatty fish, olive oil
- Blood sugar stability: Balanced meals with protein, healthy fats, and fiber
- Hydration: Even mild dehydration can lower HRV and increase stress
- Moderate caffeine: Limit to morning hours and monitor individual response
Research highlight: Research in Nutrients found that adherence to a Mediterranean diet pattern was associated with higher HRV and lower markers of stress.
Creating Your HRV-Based Stress Management Plan
Daily Practices
- Morning HRV check: Use your morning HRV reading to gauge your stress level and recovery status
- Breathing breaks: Schedule 3-5 minute breathing sessions throughout the day
- Stress journaling: Note activities or situations that correlate with HRV changes
Weekly Practices
- HRV trend review: Look for patterns in your weekly data
- Recovery sessions: Schedule dedicated recovery activities based on HRV trends
- Nature exposure: Spend time outdoors, especially in natural settings
Monthly Practices
- Lifestyle assessment: Review how changes in work, relationships, or habits affect your HRV
- Stress inventory: Identify ongoing stressors that may need addressing
- Adjust strategies: Refine your approach based on what the data shows is working
Case Studies: HRV and Stress Management Success Stories
Executive Burnout Prevention
John, a 42-year-old executive, used HRV monitoring to identify that his stress levels were highest on days with back-to-back meetings. By implementing 5-minute breathing breaks between meetings and blocking "recovery time" in his calendar, he improved his HRV by 15% and reported feeling more in control of his stress.
Anxiety Management
Sarah, a 35-year-old with generalized anxiety, used HRV biofeedback training to develop greater awareness of her stress response. After eight weeks of daily practice, her resting HRV increased by 12ms, and she reported a significant reduction in anxiety symptoms.
Conclusion
HRV monitoring provides a unique window into your body's stress response, allowing you to objectively track your stress levels and the effectiveness of management strategies. By establishing your baseline, recognizing patterns, and implementing evidence-based interventions, you can use HRV to develop a personalized approach to stress management.
Remember that improving HRV and stress resilience is a journey, not a destination. Small, consistent actions typically yield better results than occasional major changes. Use your HRV data as feedback to refine your approach over time.
Ready to start monitoring your HRV for stress management? Check out our recommended devices:
- Whoop for comprehensive stress and recovery tracking
- Oura Ring for sleep-focused HRV monitoring
- Polar H10 for accurate spot-checks and HRV training
Note: This post contains affiliate links. We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through these links at no additional cost to you.
Ready to improve your health with HRV monitoring?
Check out our top recommended devices below and start your journey to better health today.